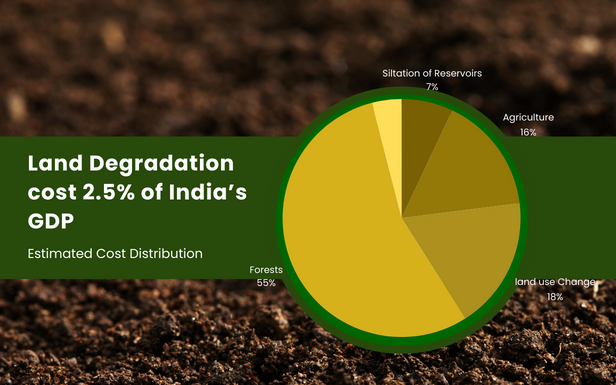
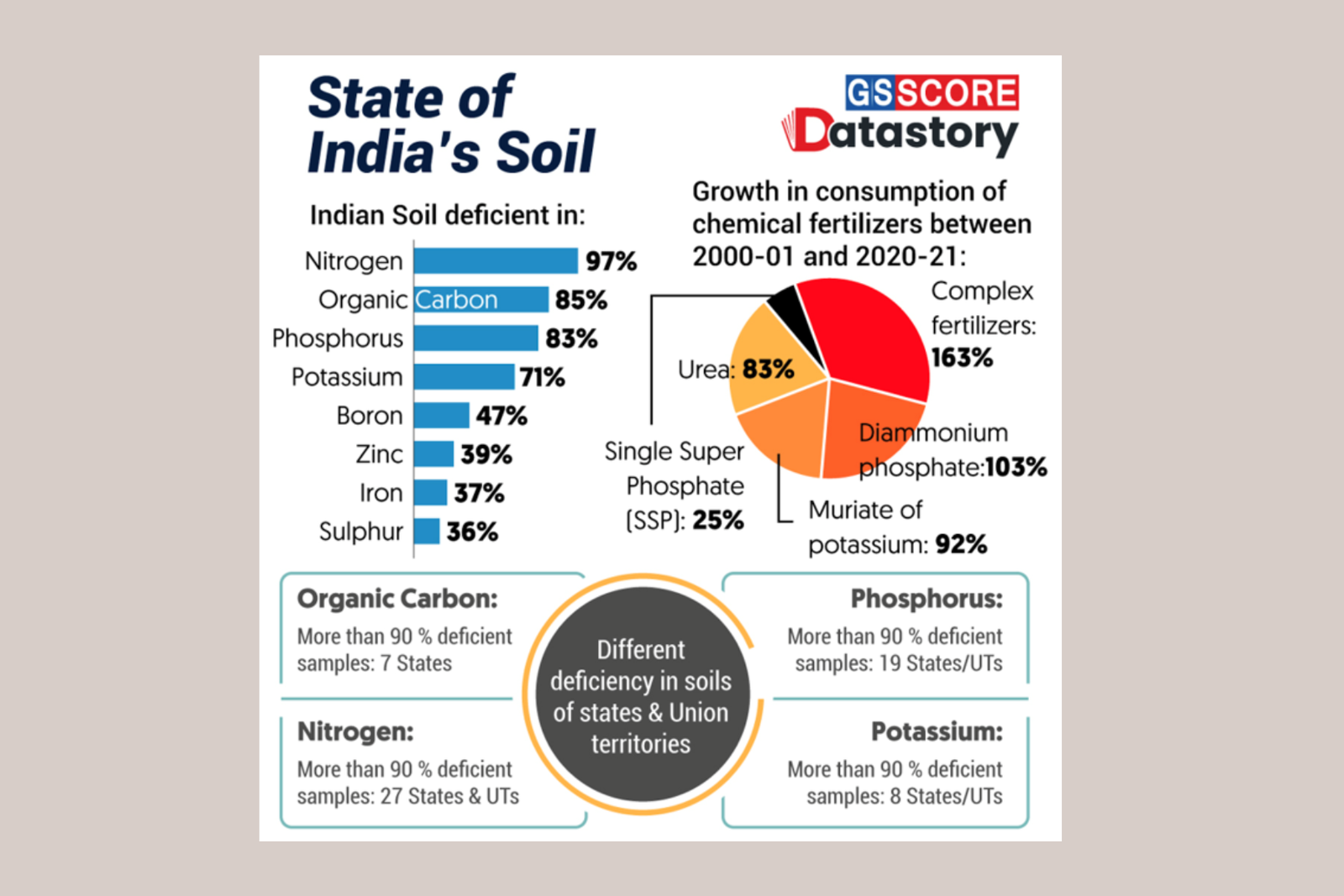
India is losing fertile soil at an alarming pace. It is estimated that the country loses a staggering 5,334 million tonnes of soil every year due to erosion caused by factors such as deforestation, intensive farming practices, and heavy rainfall. This loss of topsoil not only removes valuable nutrients but also reduces the soil’s capacity to hold water and support plant growth. If left unaddressed, this problem could have adverse effects on agriculture, which is the major source of livelihood for a significant portion of the population. Conservation measures are urgently needed to mitigate soil erosion and preserve the fertility of India’s land.
It is estimated that almost half of the country’s total landmass needs conservation measures to check soil erosion. This highlights the severity of the issue and the urgent need for action. Without proper measures in place, the problem of soil erosion could worsen, leading to even more significant consequences for the agricultural sector and the livelihoods of millions of people.
Efforts to address this issue should focus not only on preventing soil erosion but also on improving soil health and fertility. This can be done through sustainable farming practices, such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and the use of organic fertilizers. Additionally, promoting awareness and education among farmers about the importance of soil conservation can play a crucial role in preserving the fertility of India’s land.
The government, along with various stakeholders, should take proactive steps in implementing policies and programs that encourage sustainable land management practices. This may include providing financial incentives and support to farmers who adopt soil conservation practices, promoting research and development in the field of soil health, and strengthening regulations to prevent soil degradation.
Preserving the fertility of India’s land is not only crucial for ensuring food security and sustainable agriculture but also for mitigating the impacts of climate change. Healthy and fertile soil acts as a natural carbon sink, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming.